In the fast-paced digital world of 2025, website performance isn’t just a luxury—it’s a necessity. Whether you’re running a WordPress site, a custom PHP application, or a large e-commerce platform, speed directly impacts your SEO rankings, user experience, and conversions.
One of the most effective—yet often overlooked—tools for speeding up PHP websites is OPcache. Let’s learn what it is, how it works, and why you should enable it now.
What Is OPcache?

OPcache is a built-in PHP caching engine that stores pre-compiled script bytecode in the server’s memory.
Simply put, every time a PHP file is run, it doesn’t need to be recompiled from scratch. Instead, OPcache keeps a “ready-to-run” version in RAM, allowing PHP scripts to execute faster and more efficiently.
Learn more about OPcache on the official PHP Manual
How OPcache Works
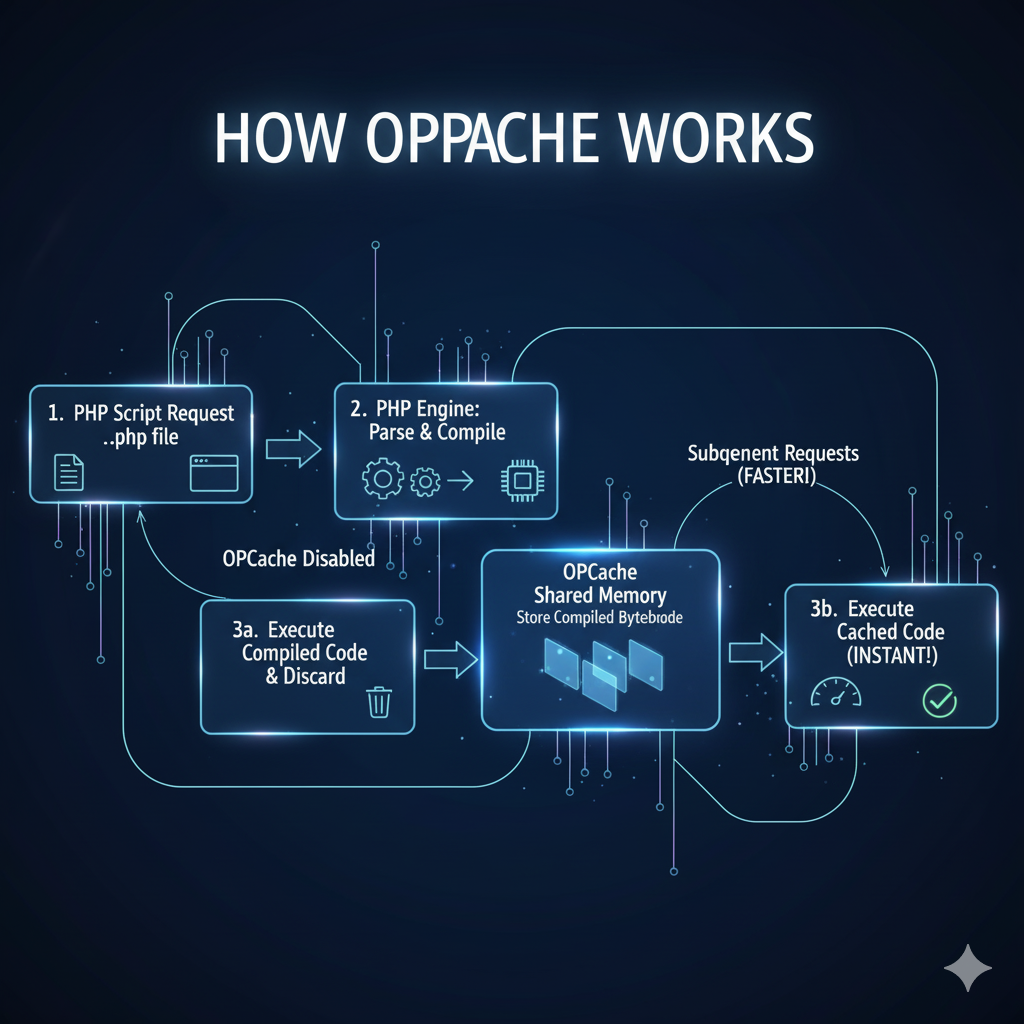
Normally, when a PHP script runs:
- PHP reads the script file.
- It compiles the code into machine-readable “opcode.”
- Then it executes the compiled code.
With OPcache enabled:
- PHP compiles once and reuses the compiled result.
- The bytecode is stored in server memory (RAM).
- Future requests for that file skip the compilation step, saving CPU time and disk access.
Benefits of Enabling OPcache
- Faster Website Loading
OPcache can reduce PHP execution time by up to 70%, making your site load much faster.
- Lower CPU Usage
Since the scripts are cached, your server does less compilation work.
- Better Scalability
Handle more concurrent users with the same server resources.
- Reduced Disk I/O
PHP scripts are run from memory instead of reloading them from disk each time.
- Improved SEO and Conversions
Google loves fast sites – OPcache helps improve your core web vitals and user engagement.
How to Enable OPcache
OPcache is already present in most modern PHP installations.
To check if it is enabled, create a PHP info file:
<?php phpinfo(); ?>Search for “opcache” in the results.
If it isn’t enabled, you can turn it on by editing your php.ini file:
opcache.enable=1
opcache.memory_consumption=256
opcache.interned_strings_buffer=16
opcache.max_accelerated_files=10000
opcache.revalidate_freq=60
opcache.validate_timestamps=1Then, restart your web server:
sudo systemctl restart apache2or
sudo systemctl restart nginxPro Tip: Fine-Tune for Maximum Performance
For high-traffic or WordPress-heavy environments:
- Increase
opcache.memory_consumptionto 512M or more. - Set
opcache.max_accelerated_filesto 20000+ for larger sites. - Disable timestamp validation in production:
opcache.validate_timestamps=0(Just remember to clear cache manually after updates.)
How to Monitor OPcache
You can use tools like:
- OPcache GUI (open-source dashboard)
- PHP OPcache Status plugins for WordPress
- Command-line tools:
php -i | grep opcacheMonitoring helps you track memory usage, hit rates, and performance improvements.
Final Thoughts
In 2025, optimizing your PHP website isn’t optional—it’s essential to staying competitive.
Enabling OPcache is one of the easiest and most effective performance enhancements. It’s free, built-in, and requires minimal configuration.
So, if you haven’t done so yet – enable OPcache today and experience the difference in speed immediately.
Bonus Tip
If you’re running WordPress, combine OPcache with:
- Object caching (Redis or Memcached)
- Page caching (Varnish or Nginx FastCGI)
for maximum performance gains.